Nov 5, 2025
Kote Beridze
ETL tools: a straightforward explainer
I am Kote from Tower’s growth team and I am writing a series about the basics of data engineering. In this post, I'll walk you through the main ideas behind ETL.
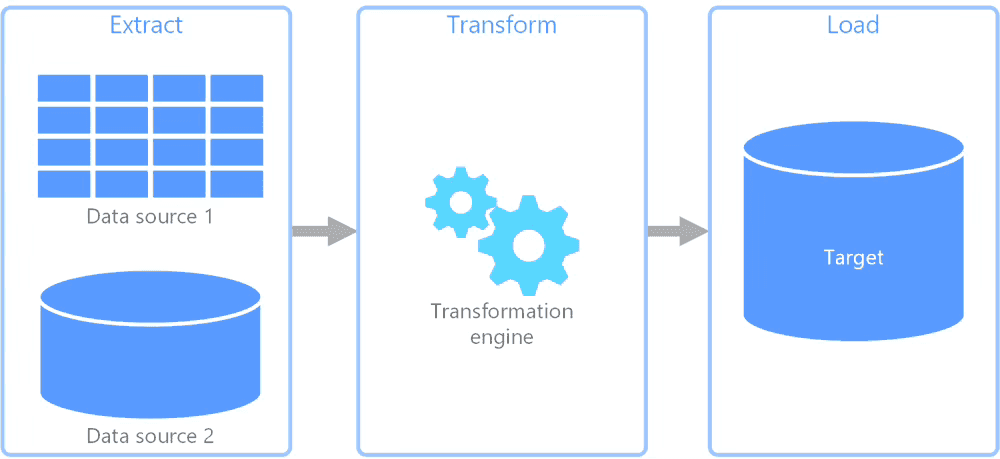
Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) is the process of extracting data from operational databases and loading it into a data warehouse or another database. ETL can also process unstructured data from logs or documents and store it in a structured format, such as a data lakehouse.
ETL is essential for data integration and analytics, and it's a key idea in data engineering. Many companies focus on doing it well. While some online discussions make it sound easy, ETL is actually a complex process.
Writing this post helped me see how Tower fits into the ETL world. By the end, you'll understand the main steps of ETL and be able to start thinking about which tools could work best for you.
What is ETL, and what do ETL tools do?
Raw data is often spread across different locations. To collect, organize, and store it together, you need to follow a few steps.
Step 1: Extract the data. This means pulling it from sources like data lakes, APIs, databases, or devices. For example, to study customer churn, you would collect customer interaction data from your website or other sources.
Step 2: Transform the data. After collecting it, ensure it maintains a consistent format and quality. This could involve filtering, cleaning, aggregating, enriching, or setting up a schema. You shape the data to fit your business needs. In the churn example, you would normalize, enrich, and highlight patterns in the data.
Step 3: Load the data into its final destination. This could be a data warehouse or a data lakehouse that your analytics users can access easily. They will use this data to find insights.
Any business that wants to make better decisions with data - such as tracking medical devices, forecasting electricity use, or running analytics - needs a robust ETL process. This also means having reliable ETL tools.
A good ETL tool connects to multiple data sources and targets, handles large volumes of data effectively, checks data quality, and makes building and maintaining pipelines easier. The right tool can save you hours by automating data integration.
Modern ETL tools are built to scale, so they can handle larger volumes of data without slowing down. This helps keep your business running smoothly. With a reliable, easy-to-use tool, you get accurate reports and analysis, which are key to making data-driven decisions.
So, what are some good tools for each of these purposes?
Depending on your needs, you have to make a few choices before picking ETL tools for your organization. Do you want full-stack ETL tools that do everything, or specialized tools you can connect together? Are you looking for specific libraries, or do you want tools that work with any system?
ETL vs ELT - what’s the difference?
Before making those choices, you should decide whether to use ETL or ELT. Lately, ELT has become more popular. In ELT (Extract, Load, and Transform), you load the data into a data lakehouse first, then transform it right in the lakehouse, using a new set of tables.
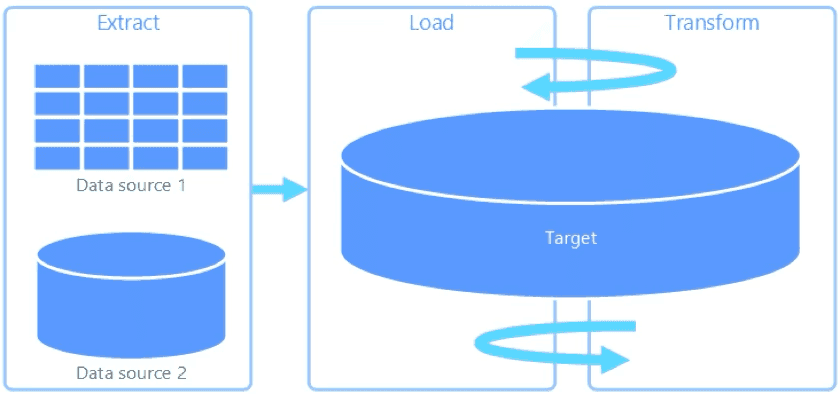
ELT has its own benefits, especially with tools that support large data warehouses and lakehouses. These systems have built-in data transformation engines, so you can load data quickly and access it in real time. They use the storage system's computing power, which saves your local resources. However, ELT tools do have some limits compared to ETL tools.
ETL tools work well for older systems or when you have strict compliance needs. If you have sensitive data that must be masked before storage, ETL helps you meet this rule. For example, you can't store raw medical data in Iceberg, so you transform it to remove personal details before loading. ETL also lets you use your own resources for transformation, which can help you save on compute costs at the destination.
Full-stack ETL tools vs specialized tools
Now that we've covered what ETL is and how ETL tools help, let's look at what these tools actually are.
When I talk about "ETL tools," I mean a whole ecosystem of data tools. Some are full-stack, handling everything from extraction to loading in one platform. For example, enterprise suites like Informatica PowerCenter or Microsoft SSIS offer drag-and-drop interfaces, connectors, transformation features, and scheduling tools in one package. I call these "One-Stop Shop" solutions. Their main advantage is convenience and support, which is great for large companies with complex needs and bigger budgets. The downside is cost and less flexibility. These tools can be expensive and may lock you into their system. Lately, more vendors are offering full-stack solutions, like Fivetran's recent acquisition of dbt.
The other option is to use specialized tools for each part of the ETL process. This lets teams build a stack of tools they like for each stage. For example, you might use one tool just for extracting and loading data, and another for transforming it. A common approach today is to pair a dedicated Extract-Load (EL) service with a separate transformation service.
You can also use open-source pipelines. For example, you might extract data with a tool like Airbyte or Singer, then transform it with a Python script or a Spark job, and use Tower to manage the process.
Why choose multiple specialized ETL tools over one?
The main benefits are flexibility and often lower costs. You can choose the best tool for each job. This mix-and-match approach works well with modern cloud setups and the modular style of today's data stacks. The downside is more complexity, since you have to manage and coordinate more tools. That's where workflow orchestrators like Tower or Apache Airflow help by scheduling and organizing everything, making things run more smoothly. In short, you trade convenience for more control.
It's important to know that the industry is changing quickly. As mentioned, Fivetran's acquisition of dbt is a big deal. At the same time, new open-source projects are coming out that connect different stages of ETL. For example, open libraries now offer connectors, and transformation engines like Polars (a fast alternative to Pandas) are becoming popular. Connectors - the pieces of code that pull data from specific sources - are often called the "unsung heroes" of ETL. Without good connectors, even the best transformation engine can't do its job.
At Tower, we aim to be your reliable partner in your data journey. Building a custom ETL stack is your strength, and you know what works best for your team. While you have control over your complex setup, we know it can get overwhelming. That's where Tower comes in to take care of the hard work, so you can focus on what matters most. Check out our aGnostics case study to learn more.
Now that we've covered what ETL is and what ETL tools do, we can talk about specific tools we recommend. Stay tuned for Part 2 of this series, which will look at the ETL tools landscape.